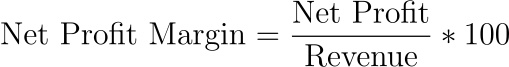
Key KPIs all finance teams should be tracking
Learn more ->
Webinar Alert 🚨
How top FP&A teams create forecasts that drive conversions - May 2nd at 12 PM ET
🔥 Register Now →The Net Profit Margin, also referred to as an organization’s bottom line, is the specific KPI that measures a company’s efficiency at generating profit rather than revenue.
This financial metric is often expressed as a profit percentage and illustrates how much of each dollar earned translates into actual profit. The profit margin calculation allows investors to see whether or not an organization’s management is generating enough profit from the cost of sales. Ultimately, the net profit measures the financial health of a company for business owners and investors.
The net profit margin can be seen on two different financial statements, the income statement and the profit and loss statement. Once your company brings in its sales revenue, you can then pay off its direct costs associated with production such as general, sales, and administrative expenses, depreciation, amortization, interest, and taxes.
To take it one step further and get a more holistic view of your company’s financial health, consider analyzing other metrics including cash flow and gross profit margin.
The net profit margin is calculated by subtracting business expenses from sales. These types of operational expenses are any variable costs associated with running a business such as rent, utilities, insurance, marketing, and any other cost of production. Sales are the total amount of money received for products sold. This figure can be broken down further to show which parts of the business generated the most profits.
The net profit margin formula is as followed:
Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100
In addition to serving as a measure of profitability, this financial ratio provides insight into how effective management is at generating more profit. A high net profit margin indicates that the company has been successful at reducing its operational costs while increasing its revenues. This can give an organization a competitive advantage when faced with intense competition. Conversely, a low net profit margin shows that the company has failed to reduce its operational costs while increasing revenues.
It’s also a highly used business profitability metric used for comparing the performance of two different companies. If you were to use the net profit margin for comparison purposes, be sure to use a company within your industry so that it has a similar business model as yours. This means they should hopefully have similar operating margins.
When calculating the net profit margin, include only those items that directly contribute to the generation of profits. For example, if a company sells products through retail outlets, then the store overhead costs should not be included when calculating the net profit margin. However, if the company sells products online, then the website hosting fees would be considered part of the operating expense.